Services
Trauma Surgery
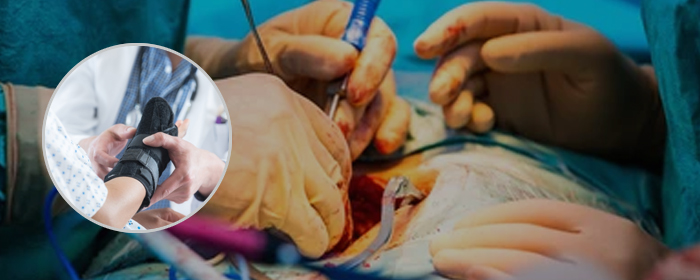
Trauma surgery is a surgical specialty that utilizes both operative and non-operative management to treat traumatic injuries, typically in an acute setting. Trauma surgeons generally complete residency training in general surgery and often fellowship training in trauma or surgical critical care.
What Does a Trauma Surgeon Treat?
Trauma surgeons are qualified to diagnose and surgically repair trauma caused by injuries and illness. They must quickly evaluate a person’s condition and determine what type of operation-if any-is necessary.
Conditions a trauma surgeon might treat include:
Blunt or Penetrating Trauma Blunt trauma is any injury from a forceful impact. Common causes are motor vehicle crashes, falls, or assaults. Penetrating trauma is an injury from an object that pierces the skin and other tissues, including gunshot wounds, stab wounds, and farm equipment injuries.
Burns You may need a trauma surgeon to treat severe burns, such as thermal burns, chemical burns, frostbite, and inhalation injury burns. Treatment options can include emergency surgery, skin excision, and skin grafting procedures.
Acute Care & Emergency General Surgery Conditions Sometimes people have unexpected medical emergencies that need immediate surgical intervention. Trauma surgeons can treat appendicitis, diverticulitis, cholecystitis, a perforated bowel, a perforated ulcer, abdominal abscesses, incarcerated hernias, and bowel obstructions.
Surgical Critical Care Conditions Trauma surgeons also perform surgical critical care procedures on patients who were already in the hospital for another surgery or procedure. This includes people with sepsis, respiratory failure, multi-organ failure, or coagulopathy.
Procedure
The procedures we use depend on your condition, but may include
Exploratory laparotomy
Emergency thoracotomy
Resuscitation
Chest wall stabilization
Complications
Failure to provide trauma surgery immediately in cases where it is required may lead to a wide range of long-term problems, which include, but are not limited to, limb amputation, internal organ damage, neurological deficits and loss of function. Fortunately, advances in medicine and technology over the past few decades have allowed for the improvement of understanding the events that cause morbidity and mortality in severe injuries.